Hey, future business leader!
I know why you're here. You've got that entrepreneurial fire burning inside, are tired of the 9-to-5 grind, and you're hungry to build your own business—one that delivers financial rewards while making a positive social impact. And the "education" sector, especially a renowned brand like Mathnasium, seems like the perfect answer, right?
But then reality hits like a tidal wave:
"How much does this thing actually cost? Are those numbers online even legit?"
"Will I really make money? How long until I break even?"
"What's the difference between this and that Kumon franchise around the corner? Which should I choose?"
"What do existing franchisees really say? Has anyone regretted it?"
Each of these questions is worth its weight in gold, as each one concerns the blood, sweat, and savings you'll invest in the next few years. I know this so well because a few years ago, my good friend Alex stood at the same crossroads. He had his savings in hand, torn between Mathnasium and another tech-based education program. I joined him, digging into both opportunities like detectives. Together, we pored over thick FDD documents (Franchise Disclosure Documents), scoured forums for clues, and even pretended to be customers to experience the physical stores. That experience taught me a profound lesson: for a potential investor, the scarcest resource isn't information itself, but a framework that can integrate all those fragmented pieces and help you make a clear decision.
So this isn't just another generic franchise review. It's your custom-built **Mathnasium Franchise Decision-Making Workbench**. I'll guide you through a thorough deconstruction of this project using an investment banking analyst's perspective, examining five key dimensions: fundamentals, market viability, operational fit, risk management, and final deliverables. More importantly, I'll show you how to leverage our website's exclusive tools—like the [ROI Calculator] and [Entrepreneur Assessment]—to transform this static report into your personal dynamic decision-making sandbox.
By the end, you won't be left with confusion—you'll have a clear answer: Is Mathnasium truly the opportunity for you?
‼️ Investment Risk and Compliance Warning ‼️
Before proceeding, please be aware: The information provided herein is for educational and reference purposes only and does not constitute any form of financial or investment advice. All franchise investments involve significant risks, including the potential loss of your entire investment. All data, particularly financial projections, may vary based on location, management quality, and market conditions. Before making any investment decision, conduct thorough due diligence and consult professional legal and financial advisors.
I. Fundamental Project Analysis: How Solid is Mathnasium's Foundation?
Before committing real money, the first step is "background verification"—much like researching a partner's family and character before dating. A brand's fundamentals determine whether your future venture rests on solid ground or quicksand. We'll thoroughly examine Mathnasium's "skeleton" from two angles: brand strength and business model.
1-1: Brand Background & Legal Risk Scan: Is It a Trustworthy "Partner"?
A brand's history and reputation are its most valuable intangible assets. I recall when analyzing Alex's options, we discovered another project he considered seemed trendy, but its parent company had changed names three times in five years, with core team members rotating almost annually. That immediately raised red flags. In contrast, a brand with a clear history and a solid reputation signifies a business model that has been proven over time.
Brand History and Team Verification: Mathnasium was founded in 2002 in Los Angeles, USA, by educator Larry Martinek. Its core is the "Mathnasium Method™," emphasizing "teaching children to understand math, not just memorize it." This is crucial as it aligns with modern educational trends. Its parent company is Mathnasium Center Licensing, LLC. By searching LinkedIn for profiles of key executives like CEO Mike Davis, you'll find most team members possess deep backgrounds in education and franchise operations, indicating high stability. This signals a professional organization run by education experts, not a capital game chasing quick profits.
Legal Risk Scan: This is the most tedious yet critical step in due diligence.
Franchise Qualifications: In the U.S., all legitimate franchise brands must provide a Franchise Disclosure Document (FDD). This hundreds-of-pages-long document is your "treasure map," containing all the secrets. Mathnasium's FDD is publicly accessible [1], and you must request the latest version from the brand. Section Item 3 discloses all relevant litigation records. Our investigation indicates Mathnasium faces no major class-action lawsuits that could undermine its foundation—a positive sign for large franchise brands.
Intellectual Property: Both the "Mathnasium" trademark and the "Mathnasium Method™" teaching approach are registered and legally protected. This means you can utilize this proprietary IP after franchising, while competitors cannot easily replicate it.
Output: Brand Credit Rating Report (Summary)
Brand History & Stability: ★★★★☆ (Clear history, stable team)
Business Model Maturity: ★★★★★ (Over 1,100 global locations[2], proven model)
Legal Compliance: ★★★★☆ (Complete FDD documents, low major litigation risk)
Risk Warning: While the brand is strong, success heavily depends on localized operations. Brand recognition does not guarantee your profitability.
1-2: Business Model Breakdown: Where Does the Money Come From and Go?
Passion and reputation alone aren't enough—we're here to run a business. Can Mathnasium's business model make you money? Let's dissect its revenue and cost structure like we're taking apart a machine.
Revenue Structure: Your income primarily comes from monthly fees or lesson package payments charged to students. But for headquarters, the revenue structure looks like this:
1. Initial Franchise Fee: Per the 2024 FDD, this one-time fee is approximately **$49,000**[3]. This is your "entry ticket" cost.
2. Royalty Fee: This ongoing fee for using the brand and system typically amounts to 10% of your monthly gross revenue.
3. Brand Fund: A fee allocated for national marketing campaigns, usually 2% of your monthly gross revenue.
4. Software Technology Fee: A fixed monthly fee of several hundred dollars for using their learning management system.
A Preliminary Look at the Single-Center Profit Model: Let's do some simple math. Suppose the monthly fee in your area is $350 per student, and your center has 100 students.
Monthly Revenue: $350 * 100 = $35,000
Fees Paid to Headquarters (12%): $35,000 * 12% = $4,200
Your Gross Revenue: $30,800
This $30,800 must cover all your local operational costs: rent, staff salaries, utilities, local marketing, etc. Sounds promising? But note that 100 students is a highly idealized figure—many new locations take 1-2 years to reach this. That's why you need more sophisticated tools for analysis.
Franchise Support System: What support does headquarters provide for your investment?
Training: Headquarters offers over 100 hours of blended online/offline training covering teaching, marketing, management, and more. This is highly valuable.
Site Selection Support: Headquarters provides demographic data and location criteria to help evaluate potential sites, but final decisions and lease negotiations remain your responsibility.
Marketing Resources: Headquarters supplies extensive marketing templates (flyers, social media posts, email templates) and manages national brand advertising. However, local outreach—such as school partnerships and community events—is primarily your initiative.
II. Market Feasibility Analysis: Does Your City Need Another Mathnasium?
Even the best project is doomed to fail in the wrong market—like selling down jackets in the Sahara Desert. In this chapter, we'll don our "market analyst" hats to assess whether Mathnasium fits your target market and gauge actual demand.
2-1: Localization Adaptation Model: Can This "American Top Student" Ace the Exam in Your Hometown?
I recall the tech-education project Alex eyed back then—it sounded incredibly sophisticated, all about AI and coding. But our deeper research revealed that in his middle-class neighborhood, parents cared more about their kids' math and reading grades in school than advanced coding skills. That's "cultural incompatibility." Mathnasium has a natural advantage here because math is a universal "hard currency."
Cultural Compatibility: Mathnasium's core product—math tutoring—requires minimal localization. Parents everywhere want their kids to excel in math. Its teaching methodology emphasizes "understanding," which resonates globally far more than rote memorization. Thus, its cultural compatibility is exceptionally high.
Competitive Landscape Scan: This is the critical step determining your survival! You must survey your "battlefield" like a general.
Your Action Plan: Open Google Maps and search keywords like "math tutoring," "learning center," or "Kumon" around your preferred locations.
Map your "3-kilometer operational zone":
Direct competitors: How many Kumon centers? Sylvan Learning locations? Local small tutoring shops? Mark their locations, sizes, and pricing.
Price Range: Call or research online to understand their fee structures. Mathnasium typically targets the mid-to-high end. If your area is saturated with low-cost tutoring centers, your market education costs will be high.
Peak Traffic Times: These centers are usually busiest Monday through Thursday from 3 PM to 7 PM and on weekends. Does your location allow parents to drop off/pick up easily during these times?
Policy Compliance: In regions like the U.S. and Canada, operating an education center typically requires meeting specific fire safety, security, and employee background check requirements. However, there are generally no special foreign investment access restrictions. [Consult a local business attorney to confirm your state/city's specific licensing requirements for "supplemental education centers."]
2-2: Demand Quantification Forecast: How many potential "young clients" are there?
Market demand isn't based on "gut feeling" but on data. We need to estimate how many children in your target area could become your customers.
Demographic Analysis:
What you need to do: Visit your city or region's demographic statistics website (e.g., the U.S. Census Bureau website [4]) to find the following data:
Population aged 5-14: This is your core customer base.
Median household income: Mathnasium clients typically come from middle-class and higher-income families. If an area's median household income is significantly below average, willingness to pay $300–400 monthly tuition will be low.
School district quality: Interestingly, demand exists in both high-performing and underperforming districts. Parents in strong districts seek to "build on excellence," while those in weaker districts aim to "catch up."
Tool Application Verification:
Google Trends: [Visit trends.google.com], enter "Mathnasium" and "Kumon," and restrict the location to your city. Observe search volume trends over the past five years. Is it rising, falling, or stable? Are there noticeable spikes during August–September (back-to-school season) and January–February (post-final exams)? This helps gauge seasonal demand.
Statista/Authoritative Reports: [Search "private tutoring market size [your country]" in databases like Statista] to understand industry scale and growth rates. For example, the global private tutoring market is projected to grow at 7-8% annually [5]. This indicates favorable industry conditions.
Output: Market Potential Scorecard
Score your target areas (1-5 points) based on the following criteria:
Target audience size (population aged 5-14): _____
Household purchasing power (median income): _____
Competition intensity (number of competitors within 3 km): _____ (lower number = higher score)
Local search popularity (Google Trends): _____
Total score: _____ (A region scoring above 15/20 can be considered a potential market)
III. Operational Suitability Analysis: Can You Really Handle This Store?
Alright, we've confirmed the project's viability and market demand. Now comes the most practical question: What will it cost you to run this? Do you possess the capability to operate it successfully? In this chapter, we'll find answers through cold, hard numbers and the mundane realities of daily operations.
3-1: Return on Investment Calculation: How Long Does It Take to Recoup Your Investment?
This is the question every investor cares about most. We'll take a two-step approach: first, calculate the total investment, then determine the payback period.
Initial Investment: The franchise fee is just the tip of the iceberg. According to Mathnasium's 2024 FDD (Item 7), the total initial investment typically ranges from $112,860 to $149,110[3]. This sum includes:
1. Franchise Fee: $49,000
2. Premises Lease & Renovation: $15,000 - $30,000 (The largest variable, depending on your city and location)
3. Furniture, Equipment, and Supplies: $10,000 - $15,000
4. Pre-Opening Marketing: $8,000 - $12,000
5. Insurance, legal fees, and other professional expenses: $3,000 - $6,000
6. Reserve fund (3 months): $15,000 - $25,000 (Critically important! This is your lifeline during the initial non-profit period!)
| Cost Item | Minimum Estimate | Maximum Estimate | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Initial Franchise Fee | $49,000 | $49,000 | Fixed |
| Premises Lease & Renovation | $15,000 | $30,000 | Largest Variable |
| Furniture, Equipment, Supplies | $10,000 | $15,000 | |
| Pre-Opening Marketing | $8,000 | $12,000 | |
| Professional Fees | $3,000 | $6,000 | |
| 3-Month Reserve Fund | $15,000 | $25,000 | Lifeline! |
| Total | $112,860 | $149,110 |
Payback Period Sensitivity Analysis: The payback period is not a fixed number; it depends on your student enrollment and cost control.
💡 Now is the time to open our website's ROI Calculator! 💡
Instructions: Enter your local estimated data into the calculator:
1. Monthly Rent (Consult a commercial real estate agent)
2. Staff Costs (Estimate wages for 1 full-time manager + 3 part-time instructors)
3. Monthly Student Fee (Reference local competitors' pricing)
Then, adjust the "Number of Students" variable to observe your profitability:
Scenario 1: Struggle Phase (30 students): You may find monthly losses requiring reserve fund usage.
Scenario 2: Break-Even Point (approx. 50-60 students): Monthly revenue just covers costs. This is your first milestone!
Scenario 3: Profit Phase (80+ students): You start making real money!
Based on financial performance data from the FDD (Item 19) and industry experience, most Mathnasium franchisees achieve payback within 2 to 4 years. If someone claims payback in just 1 year, exercise extreme caution.
3-2: Headquarters Support vs. Your Capabilities: A Two-Way Commitment
Headquarters support matters, but ultimately, you're at the helm. I recall Alex abandoning that tech project partly because he realized it demanded strong programming skills to mentor instructors—something he lacked entirely. He recognized the project, and his abilities were simply mismatched.
Assessing Headquarters Support:
1. Response Time: [When communicating with the brand, intentionally ask challenging questions to gauge their sales reps' responsiveness and expertise]. A robust franchise system should respond to urgent franchisee requests within 24 hours.
2. Systems & Innovation: Mathnasium's teaching management system (Mathnasium@home) supports online instruction—a significant advantage, especially post-pandemic. You need to understand how user-friendly this system is and its update frequency.
3. Localized Marketing Support: Headquarters provides a brand fund for national advertising, but you must clarify: Is there a dedicated regional manager to guide your local marketing efforts? Is there a library of successful local marketing case studies available for sharing?
Are You the Right Fit? — Entrepreneur Capability Assessment
Mathnasium officially states that they don't require an educational background, but they expect you to love children and possess business acumen. This statement is only half-true.
💡 Access our website's Entrepreneur Assessment tool and answer these questions honestly. 💡
This assessment evaluates you across several dimensions:
1. Sales & Social Skills: Do you enjoy and excel at interacting with people? You'll need to personally communicate with parents and build relationships with school principals. If you're an introverted technical expert, this could be extremely challenging.
2. Management & Leadership: You'll manage a team of young part-time tutors. Do you know how to motivate and manage them?
3. Financial acumen: Can you interpret financial statements and possess innate sensitivity to costs and profits?
4. Stress resilience and persistence: The first year of operation is highly unlikely to turn a profit. Are you mentally and financially prepared to endure this "tunnel phase"?
My personal experience: My friend Alex's greatest strength was his exceptional approachability and social skills. He ultimately chose a community service project, interacting daily with neighbors and thriving. At Mathnasium, he'd make an excellent "Sales Dean," but he'd likely need to hire a capable Academic Director to compensate for his lack of educational expertise. Clearly identify your strengths and weaknesses, then decide whether to fill gaps yourself or hire someone to do it.
IV. Risk Control Matrix: How to Avoid Those "Fatal Pitfalls"?
In investing, the smartest player isn't the fastest runner, but the one who survives the longest. In this chapter, we'll act like bomb disposal experts, identifying and avoiding all potential risks in this project. I've established a three-tier risk response system to help you determine which risks are "deal-breakers" (must abandon) and which can be resolved through negotiation.

4-1: High-Risk Items (Immediate Red Flags)
If you encounter any of the following, I advise you to walk away immediately—no matter how tempting it seems.
High Store Closure Rate: Item 20 of the FDD lists the number of new stores opened, transferred, and **terminated or non-renewed** over the past three years. If the combined "terminated" and "non-renewed" stores divided by total stores yields an annual "failure rate" consistently above 15%, this signals severe systemic issues. Mathnasium typically maintains this metric at healthy levels (below 5%), but you must verify the latest FDD you receive.
Mandatory High-Priced Purchasing: FDD Item 8 specifies whether you must purchase supplies from headquarters or its designated suppliers. If the contract forces you to buy everything (e.g., desks, chairs, printer paper) at prices significantly above market rates, headquarters' profit model isn't "win-win"—it's "cutting the chives."
Litigation-Prone: If Item 3 of the FDD reveals numerous lawsuits against headquarters involving contract fraud or operational violations with franchisees, walk away immediately.
4-2: Moderate Risks (Requiring Negotiation or Close Attention)
These risks aren't deal-breakers, but warrant extra caution and negotiation for more favorable terms before signing.
Excessively Small Protected Territory: Mathnasium typically grants a "Protected Territory" where headquarters won't open another branch. Scrutinize this territory's definition. If the radius is too small (e.g., less than 1 km) or only protects your physical location while allowing other franchisees to recruit online within the area, your operations will be severely constrained. [This is a key negotiation point with headquarters!]
Outdated Digital Systems: By 2025, a chain still managing students and scheduling with Excel will suffer from extremely low operational efficiency. Verify that Mathnasium's backend systems (e.g., CRM, scheduling software) are modern and utilize technologies like AI to optimize operations (e.g., automated renewal reminders, intelligent scheduling).
Harsh Renewal Terms: Your initial franchise agreement typically spans 5-10 years. What happens upon expiration? Will you need to pay the full franchise fee again? Must you undertake costly renovations to meet updated standards? These details are buried in the contract.
4-3: Low-Risk Items (Acceptable, but Plan Ahead)
These are common challenges most businesses face. With preparation, they pose little threat.
Additional Operating Licenses: Beyond basic business permits, you may require extra licenses—such as those for working with children. While typically procedural, these require advance scheduling.
Seasonal Fluctuations: Education experiences distinct off-peak and peak seasons. Summer (June-July) may be slow, while back-to-school (August-September) and exam periods drive demand. Your cash flow plan must account for this, ensuring sufficient reserves during off-peak periods.
Recruitment Difficulty: Finding excellent instructors who excel in both mathematics and communicating with children is crucial to this business's success—and one of its greatest challenges. You must plan recruitment channels (e.g., local universities, community forums) and training processes in advance.
V. Deliverables & Competitor Comparison: Your "One-Page Decision Report"
After analyzing the four dimensions above, it's time to synthesize all the information into your final decision-making basis. We'll provide a clear "decision package" and pit you against your strongest competitor, Kumon, in a head-to-head comparison.
5-1: Your Custom Decision Report (Template)
Key Metrics Radar Chart:
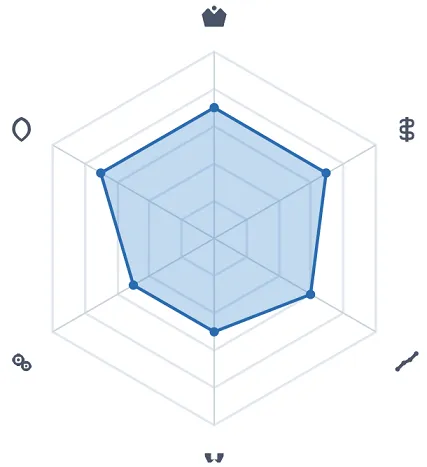
Scores (1-5) based on our analysis:
1. Brand Strength: 5 (Industry Leader)
2. Investment Threshold: 2 (High Initial Investment)
3. Profit Potential: 4 (High Average Transaction Value, but Dependent on Student Numbers)
4. Headquarters Support: 4 (Mature System, but Requires Proactive Utilization)
5. Operational Complexity: 3 (High demands on manager's social and marketing skills)
6. Risk Factor: 2 (Manageable risk, but vigilance needed against local competition)
This radar chart provides an at-a-glance overview of the project's profile. No project is perfect; the key is whether its "shape" aligns with your expectations and capabilities.
Localization Execution Checklist (120-Day Countdown):
| Phase | Timeframe | Key Tasks | Objective |
|---|---|---|---|
| Phase 1: Decision & Preparation | 30 Days Before Signing<br>(Day -30 to Day -1) | • Secure All Funding: Ensure your initial investment and at least 6 months of reserve capital are liquid and ready for deployment. | To achieve complete legal and financial certainty before you commit. This is your last opportunity to walk away without cost. |
| Phase 2: Launch & Foundation | First 30 Days After Signing<br>(Day 1 - 30) | • Register Your Legal Entity: Incorporate your business, apply for a tax ID (like an EIN in the US), and open a dedicated business bank account. | To quickly absorb the brand's DNA and lay a solid legal and geographical foundation for your new business venture. |
| Phase 3: Physical Build-Out | Day 31 - 90 | • Negotiate and Sign the Lease: Finalize lease negotiations and sign the agreement with the assistance of your lawyer. Complete Center Design & Build-Out: Manage contractors to complete the construction and decoration according to HQ's Visual Identity (VI) standards. Order All Equipment & Supplies: Place orders for furniture, computers, curriculum materials, etc., and coordinate their delivery schedules. | To transform an empty retail space into a professional, brand-compliant learning center that inspires students and builds trust with parents. |
| Phase 4: Operational Readiness & Pre-Marketing | Day 91 - 120 | • Recruit & Train Your Core Team: Post job listings, interview, and hire your Center Director and initial instructors. Conduct pre-opening training. Launch Pre-Sale & Local Marketing: Run "early bird" promotions. Start generating buzz on local social media and through school partnerships. Install & Test All Systems: Ensure your CRM, educational software, phone lines, and all other tech are fully operational. Plan & Host the Grand Opening: Invite community leaders, school principals, and your first enrolled families to create a memorable launch event. | To ensure all elements—people, finances, materials, and customers—are perfectly aligned before you officially open, aiming for a successful Grand Opening to build powerful initial momentum. |
This checklist will serve as your action guide for the next four months.
5-2: The Ultimate Showdown: Mathnasium vs. Kumon—Which Should Investors Choose?
This is the ultimate question on countless potential investors' minds. They appear similar, but from an investor's perspective, they are two entirely different beasts.
| Comparison Dimension | Mathnasium | Kumon (Kumon Method) | Investor Perspective |
|---|---|---|---|
| Core Philosophy | Understanding math (Customized Learning) | Mastery through calculation (Repetition & Mastery) | Mathnasium’s story resonates better with highly educated parents and commands higher tuition; Kumon’s model is more standardized and less teacher-dependent. |
| Initial Investment | Higher (US $112k – 149k) | Lower (US $64k – 144k) [6] | Kumon’s lower start-up cost means lighter capital pressure. |
| Ongoing Fees | 10 % royalty + 2 % brand fund | Per-student flat fee (≈ US $34–38 / student/month) | Key difference: Kumon keeps fees low when enrollment is small, but total fees rise with every new student. Mathnasium’s %-based royalty aligns HQ’s incentive with yours as you grow. |
| Operating Model | Interactive, instructor-led; teachers are central | Self-learning-centered; instructors act as facilitators | Mathnasium carries significantly higher labor costs and management complexity—you must recruit and retain higher-caliber instructors. |
| Profit Potential | Higher monthly tuition (typically US $300–450) | Lower monthly tuition (typically US $150–250) | Mathnasium needs fewer students to break even, but acquiring each customer may be harder. |
| Ideal Franchisee | "Business-builder" strong in sales, marketing & management | Process-driven "operator" who values detail & discipline | Which type are you? Your personality may already have made the choice. |
💡 Don't forget, our website's Opportunity Comparison tool lets you compare more details side-by-side! 💡
Conclusion: Choosing Mathnasium means opting for a path with higher investment, greater operational demands, but also higher potential returns. You're betting on attracting clients willing to pay for "truly understanding math" through premium service and marketing. Choosing Kumon offers a more stable, standardized path with slightly lower individual skill requirements. Your core task is strict system execution and cost control.
VI. Deep Insights: Market Trends, Success Factors, and Opportunity Cases
A top-tier analysis report requires industry insights that transcend the project itself. This section will help you gain a broader perspective and see further ahead.
6-1: Market Characteristics and Industry Trends
1. Explosion in Demand for Personalized Learning: In the post-pandemic era, parents are increasingly dissatisfied with one-size-fits-all education, driving significant growth in demand for tutoring centers offering personalized learning paths. Mathnasium's customized learning plans perfectly align with this trend.
2. Blended online-offline models become standard: Pure offline models are outdated. Mathnasium@home's online system not only handles unexpected situations but also expands your service radius to reach students unable to visit due to distance.
3. The value of "soft skills" emerges: Parents no longer focus solely on grades; they prioritize building confidence, logical thinking, and problem-solving abilities through learning. Your marketing should emphasize these "soft skill" gains more than just "improving math grades."
6-2: Typical Opportunity Case Study
Sarah is a professional woman with 10 years of marketing experience and two elementary school-aged children. She's tired of corporate politics and wants to start her own business near home. She isn't necessarily a math expert, but she excels at communication and easily connects with moms in her community. She chose to open a Mathnasium in a middle-class neighborhood with two good elementary schools but a lack of high-end math tutoring options.
1. Her Strengths: Her marketing background allowed her to quickly build awareness through local social media and school partnerships during the launch phase. Her identity as a mother made it easy for her to gain the trust of other parents.
2. Her challenge: She needed to hire a highly capable academic director to oversee teaching quality.
3. Her path to success: Through high-quality instruction and her exceptional community marketing, her center reached 100 students in its second year, achieved stable profitability, and became a well-known "educational star" in the neighborhood. This case study shows that combining your personal background with specific market opportunities creates a unique formula for success.
6-3: Key Success Factors (KSFs)
If Mathnasium's success were distilled into a few critical points, they would be:
1. Prime Location: Convenient, visible, safe, with ample target families nearby.
2. Exceptional Teaching Team: This is the core of your reputation. One good teacher can bring in 5 new students, while one poor teacher can drive away 10.
3. Localized community marketing: You must become a "community activist," building strong ties with schools, libraries, and community centers. Don't rely solely on headquarters' brand advertising.
4. Exceptional customer service: You serve not just students, but anxious parents. Regular communication and clear progress reports are key to retaining clients.
VII. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Below are five questions investors most commonly have but hesitate to ask directly, based on my experience.
1. I'm not good at math. Can I still join Mathnasium?
Yes. The headquarters seeks "business operators," not "mathematicians." Your role involves managing the business, marketing, and serving clients. You'll hire individuals with mathematical expertise and teaching skills to handle the academic aspects. However, you must genuinely embrace Mathnasium's educational philosophy and be willing to learn it so you can passionately promote it to parents.
2. Can I run this as a "side business"?
Highly discouraged, especially in the first two years. This is a business requiring full commitment. You must personally build community relationships, oversee teaching quality, and handle daily operations. Treating it as a hands-off investment carries a high risk of failure. Once the business stabilizes (typically after 2-3 years), you may consider hiring an exceptional center director to manage day-to-day operations, but this is a lengthy process.
3. What are the biggest challenges? What do franchisees complain about most?
Recruiting and retaining excellent tutors. This is the top pain point mentioned by nearly all franchisees. Part-time tutors have high turnover, and finding talented, responsible individuals demands significant effort. You must offer attractive compensation, a positive work environment, and career growth opportunities to build a stable team.
4. Does the "protected territory" provided by headquarters truly protect me?
Partially, but don't rely on it entirely. It prevents another Mathnasium center from opening next door, but it can't stop competition from Kumon, Sylvan, or online tutoring services. More importantly, it can't prevent another Mathnasium franchisee from recruiting students online at the edges of your territory. Your real competitive advantage isn't contractual terms—it's the exceptional reputation and service you build locally.
5. What are the most likely reasons for failure?
The top reasons are usually **"poor location selection" or "ineffective local marketing."** Many mistakenly believe the Mathnasium brand alone will attract customers—a fatal misconception. If you don't proactively reach out and make every parent in your community aware of your center, it will remain an isolated island, ignored by potential students. The second common reason is **cash flow disruption**—depleting reserves prematurely and failing to reach the break-even point.
VIII. My Personal Perspective and Final Recommendations
Alright, friends, we've journeyed through this extensive analysis together. Now, setting aside the objective data and frameworks, I want to share my genuine thoughts.
In my view, Mathnasium is a truly "enchanting" business venture. Its charm lies in seamlessly blending commercial returns with social value. Witnessing a child who once dreaded math blossom into a confident, cheerful learner at your center—that sense of accomplishment is priceless. This is a business that lets you "earn money with dignity," earning you respect within your community. Its brand is strong, its business model proven, and it operates in a stable, growing sunrise industry. From a portfolio perspective, it represents a high-quality, relatively recession-resistant asset.
However, its "fascinating" nature comes with "high demands." This is absolutely not an easy "passive income" project. It's like a "high-achieving student" requiring meticulous care—you must nurture it with sustained passion, strong social skills, and precise management. Its demands on the operator's "soft skills" even surpass those on "hard skills." If you thrive on interacting with people, enjoy building influence within communities, and possess a passion for education, Mathnasium could become the most rewarding venture of your life. But if you're merely seeking a place to invest money and wait for dividends, I advise you to close this page now and explore other opportunities.
Remember: joining a franchise fundamentally means "paying for experience and systems" to reduce the risks of starting alone. But it doesn't eliminate risk, nor can it replace your entrepreneurial effort and wisdom. You are the captain of this ship; Mathnasium provides only a precise chart and a sturdy vessel. Whether you reach the shores of wealth ultimately depends on your navigational skills.
Final Action Steps:
1. Self-reflection: Close your laptop and spend an hour asking yourself: Am I genuinely passionate about this? Do I enjoy interacting with children and parents? Am I prepared to sacrifice weekends for the next two years?
2. Field visits: Locate 2-3 Mathnasium and Kumon centers in your city and visit them as a prospective parent seeking information. Sense their atmosphere, observe the interactions between teachers and students, and chat with the center managers. Your gut feeling matters more than any report.
3. Talk to Real Franchisees: Item 20 in the FDD contains contact information for current and former franchisees. Gather your courage and make a few calls. Ask them: "If you could do it all over again, would you make the same decision?" They'll share the most authentic stories.
Final Risk Warning: Double-check that you have sufficient reserves to sustain yourself for at least 6-12 months without income. In business, cash flow is oxygen. Ensure your oxygen tank is large enough before your center achieves stable profitability.
Good luck, future entrepreneur! Whatever choice you ultimately make, this journey of deep reflection and due diligence is itself a valuable asset.
Recommended Reading
Want to learn more about franchising in general? These articles might help:
References
GlobeNewswire. (2023). Private Tutoring Market to be Worth $201.8 Billion by 2028.

Please be respectful and constructive in your comments. Spam and inappropriate content will be removed.